Did you know that Cranial Deformities affect 49% of children?
Grant Monaghan & Associates is the first practice in Africa to be certified and accredited to run the world renowned, American FDA approved, treatment program. Our team has successfully treated over 200 babies.
All Cranial Deformities will require intervention. The type of intervention is dependent on the severity of deformity and the age of the baby. Our focus is to screen and intervene. Timing is of the utmost importance as Cranial Deformities can only be treated between 3 and 18 months of age.
There is no evidence to support the theory that the skull will, “round out” on its own and children will not, “grow out of” a Cranial Deformity. A specialised screening must be conducted so that real, tangible measurables are documented and an intervention and correction plan can be formulated.
What is a cranial deformity?
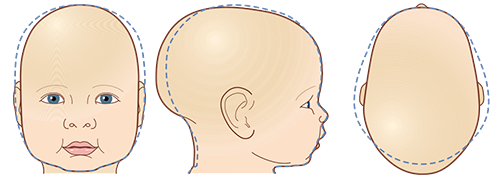
A Cranial Deformity describes a shape or symmetry change that occurs on the skull that is deemed outside of normal measurement proportions or acceptable symmetry changes. No one truly has a perfectly symmetrical face or skull, but there are acceptable proportions and if you fall outside of those parameters, you will see a knock-on rotational effect on the face.

Plagiocephaly
THE MOST COMMON CRANIAL DEFORMITY IS PLAGIOCEPHALY; PLAGIOCEPHALY CAN BE NOTICED AS EARLY AS SIX TO 10 WEEKS OF AGE.
- Asymmetrical skull shape, unilateral occipital flattening.
- Ear positioned anterior on side of occipital flattening.
- It develops when an infant’s soft skull becomes flattened in one or more area secondary to constant pressure to that portion of the skull. Studies show that 20 to 25 percent of infants that sleep on their back develop some degree of Plagiocephaly.
- Forehead may be asymmetrical / positioned anterior side of occipital flattening.
- Facial asymmetry may be present.
- May be accompanied by Torticollis, limited neck range of motion, weakness and preferential head positioning.
CAUSES OF PLAGIOCEPHALY
- Position in the womb.
- Prematurity.
- Congenital Muscular Torticollis or Positional Torticollis.
- Excessive time spent laying on the same portion of the head.
EFFECTS OF PLAGIOCEPHALY
- Misalignment of eyes and/or different eye shapes – possible astigmatism or strabismus can develop as a result.
- Asymmetry of the ears – one ear is more positioned forward than the other.
- Flattening and thickening of the jaw (mandible).
- Flattening of the cheek opposite to the flattened skull.
- Trouble with lip closure (assumption of midline) that could result in poor feeding.
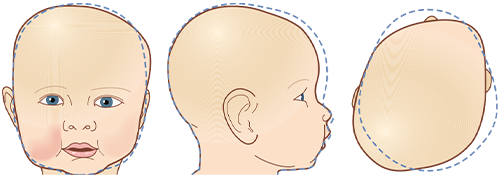
Brachycephaly
DEFORMATIONAL BRACHYCEPHALY
- Central occipital flattening.
- High and sloped skull. The head is excessively wide for its length.
- May be accompanied by a prominent, bossed forehead.
Deformational Brachycephaly with asymmetry has a combination of Brachycephaly and Plagiocephaly characteristics.
Again the shape is disproportionate wide for its length but also asymmetric, that could include the forehead and facial features.
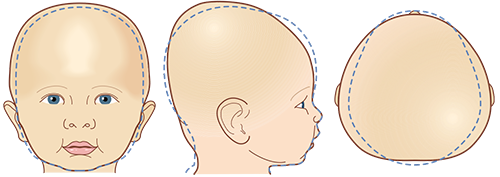
Scaphocephaly
DEFORMATIONAL SCAPHOCEPHALY
- Very elongated head shape that is excessively long for its width.
- Deformational Scaphocephaly caused by extrinsic forces is uncommon although it is sometimes seen in premature infants who are often positioned side lying, such as NICU infants.
- Scaphocephaly caused by extrinsic positioning may be confused with sagittal synostosis, a more serious deformity that usually requires surgery to correct.
Clinical Evaluation
Grant Monaghan & Associates use state of the art 4D Light scanning technology to capture a 3D image of the skull. This data is translated into a specialised program that allows the practitioner to quadrant and cross section the skull. This allows us to measure every aspect of the skull, as well as the facial features. The use of these measuring tools removes the question of opinion. The findings are based on numerical data and compared to the norms.
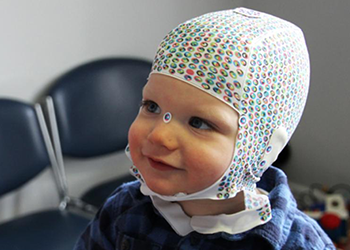
The silk scanning sock – demonstrated and worn by a patient.
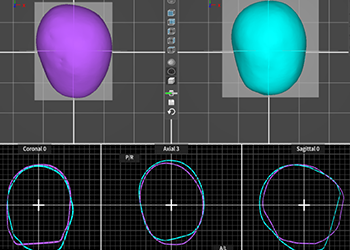
An example of the aerial view of the scanned data – a comparative before and after of a Plagiocephaly patient

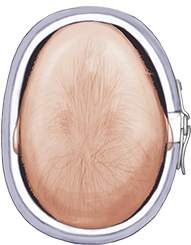
HOW DOES THE CRANIAL ORTHOSIS (HELMET) FUNCTION TO CORRECT THE CRANIAL DEFORMITY?
The Orthosis functions to provide contact over the “bossed” or protruding areas to limit continued deformation in those area and gently guides growth into areas where correction is needed.
This is a minimally invasive, external treatment that is effective and easy to use.
The helmet is easy to manage, and the child will experience no discomfort.
Each helmet is custom designed for the child’s specific presentation and needs.
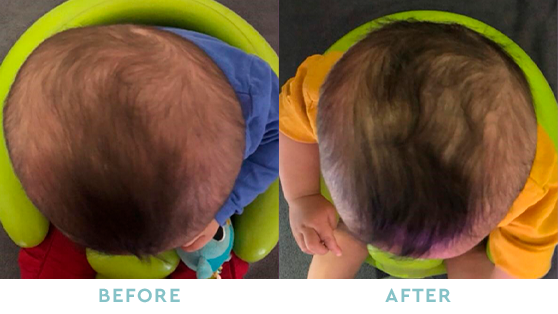
Take a Look at some of our successful, ‘Before & After” Stories
PLAGIOCEPHALY
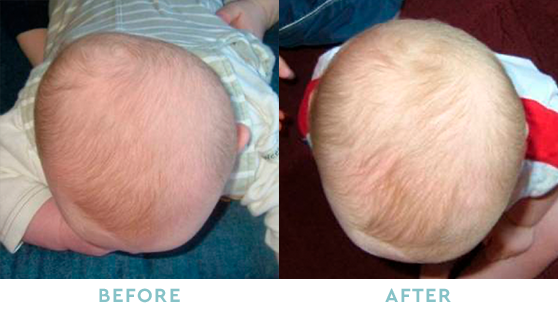
PLAGIOCEPHALY

SCAPHOCEPHALY
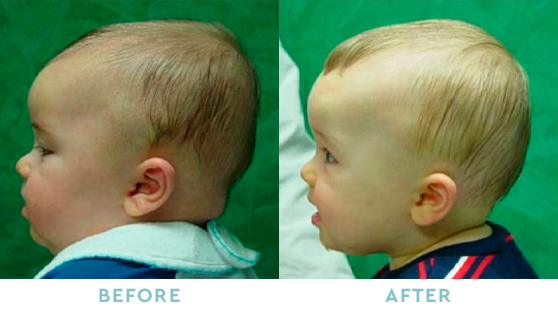
BRACHYCEPHALY

BRACHYCEPHALY
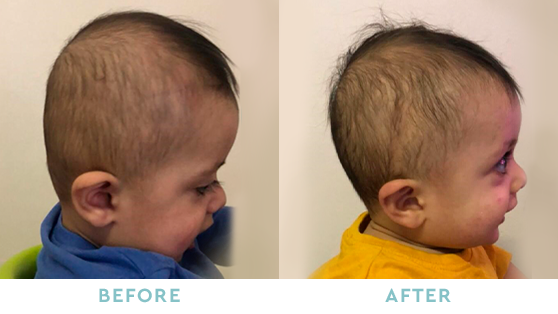
BRACHYCEPHALY
Craniosynostosis and Post-Surgical Helmets

Craniosynostosis is simply when the sutures between skull bones close before your baby’s brain is fully formed. Brain growth continues, giving the head a misshapen appearance. This can occur in one or multiple sutures.
Treating craniosynostosis involves surgery to correct the shape of the head and allow for normal brain growth. Following surgery, a Cranial Orthosis is advised following surgery to improve the shape of the skull as the bone repairs and grows. The helmet functions to guide growth into the correct quadrants to improve asymmetry and the overall appearance of the skull following surgery, as well as to protect the delicate incision following surgery.
PROTECTIVE HELMETS
Grant Monaghan & Associates are able to provide Custom Protective Helmets for patients who experience seizures or epilepsy, or who need skull protection postoperatively.
We offer a range of off the shelf protective helmets, as well as custom helmets for patients who are not candidates for ready made items.